Use the Flow controls
1. The Search control
The Search control is typically used at the beginning of a time-driven or manual flow. However, it can be placed anywhere in the flow, and can therefore be used to to cover a wide ranging use cases.
Search retrieves all orders in the system that match the respective filter settings. It then transfers them as a batch into the next flow step.
Additional settings for the Search control
| Setting | Explanation |
|---|---|
Search type |
Here, you select the object type that the control will search for. Currently, the only option available is Order, which is selected by default. This is because Flow currently processes orders only. Later down the line, Flow will be expanded to support other dataset types. |
Sort by |
Here, you select the criteria by which to sort the orders. |
Sort by |
Here, you choose whether the sorting direction is to be ascending or descending. |
Order limit |
Here, you specify the maximum number of orders to be processed per flow run, if needed. |
Handling of search results |
Here you can specify whether the flow execution should only continue with the search results from this action or whether the search results from this action should be combined with the results from previous searches and/or input actions. |
Filter settings |
Here, you define the criteria for the order search. Refer to the explanations in the section Using filter settings for the Search and Branch controls: |
Examples will be added later. |
2. The Branch control
The Branch control is typically used in flows where the flow run occurs sequentially for individual orders (stream processing). This is the case for event-driven flows.
The Branch control creates two possible flow branches at the respective flow point, determining as follows:
-
If the order meets the set filter criteria, it flows into the True branch.
-
If the order does not meet the set filter criteria, it flows into the False branch.
Note: If the order does not meet the set filter criteria and there are no actions in the False branch, then the flow run aborts for the order concerned.
Additional settings for the Branch control
| Setting | Explanation |
|---|---|
The name of the branch is "True" / "False" |
Here you can optionally enter a name for the True and False branches. If you don’t enter anything, the branches will keep the names True and False. |
Object type |
Here, you select the dataset type that the control will evaluate. Currently, the only option available is Order, which is selected by default. This is because Flow currently processes orders only. Later down the line, Flow will be expanded to support other dataset types. Note: PlentyONE Flow was designed for gradual expansion. In future, its capabilities will extend beyond order handling alone. |
Filter settings |
Here, you set the criteria for the transition to the True branch. |
|
Note on moving branches
The branch element is considered a Flow step that can comprise several actions as a control element. Branches can be placed within other branches, but there is one restriction: Due to logical relationships, a parent branch cannot be moved below its child branch using drag and drop. |
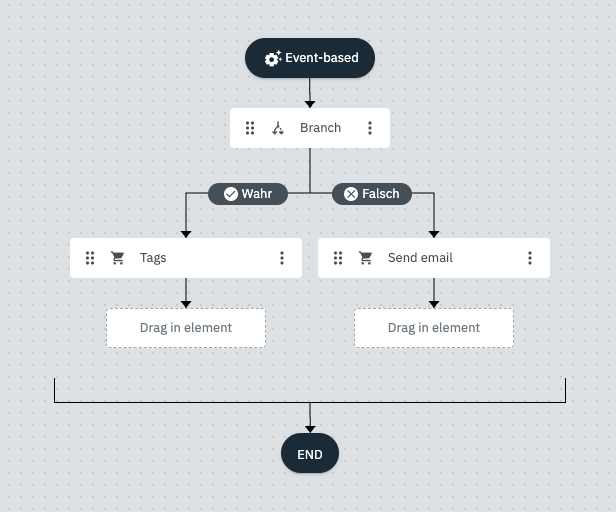
For a simple example of the branch element, let’s take a flow that checks incoming orders by order value and, depending on the order value, either sets a tag or sends an email to the sales department. The flow starts with the trigger Order of the type Sales order.
The Branch control element then checks if the order value is less than 100. If the value is less than 100, the flow goes to the True branch and a tag is set for this order with the next action. If the value is more than 100, the flow goes to the False branch and an email is sent to the sales department with the next action.
3. The Start control
The Start control is used to trigger an additional parallel flow for the orders that reach the flow step.
Additional settings for the Start control
| Setting | Explanation |
|---|---|
Additional flow |
Select the flow from the dropdown list that will be triggered in addition at that flow step. |
Processing type |
From the dropdown list, select whether the additional flow is to use batch processing (all data sets processed together, as in time-based flows) or stream processing (data sets processed individually in sequence, as in event-based flows). |
Examples will be added later. |
4. The Adapter control
The Adapter control introduces a new, related object type into the flow.
For example: You initially set your flow up to process return orders. At a certain point in the flow, you want the subsequent steps to apply to the related sales orders. To introduce the related sales orders to the flow, you would use the Adapter control.
Depending on your settings, the steps after the Adapter are executed either for both the current and new object types, or exclusively for the new object type.
|
What does the term "object type" mean?
The term “object type” refers to the category of data being processed by the flow. For example, *return order”, “sales order” and “credit note” are all different object types. |
Additional settings for the Adapter control
| Setting | Explanation |
|---|---|
Action type |
Select the type of action to be performed. Available actions: Add object type Replace object type Note: If the current order has no relation to an object of the selected type, the steps after the Adapter are skipped and a warning message for the flow run is displayed in Flow Tracker. The flow run will not be marked as Completed. Replace object type, if available Note: If the current order has no relation to an object of the selected type, the current object remains in the flow and all further steps are applied to it, as if the Adapter did not exist. |
From/To |
Select the object type to be replaced or to be added. Order to main order (original order) Notes:
|
Which orders should be loaded? (only available for order to child order) |
Specify which orders should be loaded when selecting Order to child order.
|
Error case handling |
Determine how the flow should continue in the event of errors. There are two options available:
|
|
The Adapter control is set to be gradually extended
Currently, the Adapter control allows you to add related origin orders to the flow. For example: If the flow is processing a return order, the Adapter can be used to supplement or replace the return order with the original sales order to which it relates. The Adapter is set to be gradually extended to allow for switching between a wider range of object types. |
5. Adding a control to a flow
To add a control to a flow, proceed as follows:
-
Open an existing flow or create a new flow in the Automation » Flow Studio menu.
-
Identify the flow position at which to place the control.
Note: The available positions are the empty white fields or the spots where the plus signs appear. -
Open the Controls tab in the left-hand column.
→ The tab with the available controls opens. -
Select the appropriate control. Refer to the explanations for the controls Search, Branch, and Start flow
-
Add the control to the flow by dragging it to the appropriate flow position.
-
Perform the additional settings for the control. These appear in the column to the right of the canvas. Refer to the explanations for the controls Search, Branch, and Start flow
-
Make the filter settings for a control of type Search or Branch. Refer to the explanations in the section Using filter settings for the Search and Branch controls
6. Using filter settings for the Search and Branch controls.
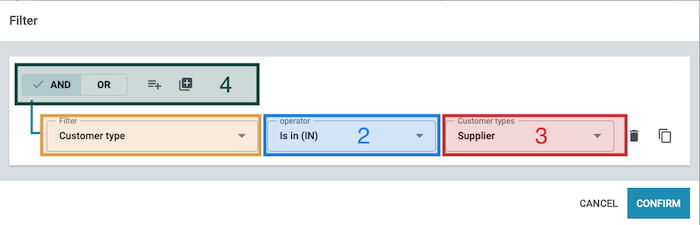
When you open the filter settings for the Search or Branch control as described in the section Adding a control to a flow, the following window appears:
-
1. Filter: Here, you select the appropriate filters. Information about the available filters can be found in the section Available filters.
Note: The selection of filters is larger for Branch than for Search. -
2. Operator: Use an operator to define the relationship between the order-specific field to be checked by the filter and the value entered in the input field (4). You can find more details about the available operators in the section Using operators.
-
3. Entry field: Here, you enter or select the values to filter by. For more information on the input field of a specific filter, refer to the Explanation column in the table Using filters.
-
4. AND & OR, conditions, and nested levels: Here, you define the filter conditions. You can find detailed information about the four functions in the section Using AND & OR, conditions, and nested levels.
6.1. Available filters
You select the filters for the Flow controls Search and Branch from a dropdown list. There, the filters are divided into categories. Click on one of the following filter categories for explanations of the available filters.
Customer filter category
| Filter | Explanation |
|---|---|
Age rating invoice address |
Filters orders based on whether the invoice address has been assigned an age rating. Additional settings:
|
Customer class |
Filters orders by customer class. Additional settings:
|
Customer rating |
Filters orders by customer rating. Additional settings:
Note: Customer ratings must be set up in the menu to appear in the dropdown list. |
Customer type |
Filters orders by customer type. Additional settings:
|
Number of orders |
Filters orders based on the number of orders previously placed by the respective customer. Additional settings: Setting 1:
Setting 2:
|
Document filter category
| Filter | Explanation |
|---|---|
Available documents |
Filters orders based on whether they contain certain documents. Additional settings:
|
Global filter category
This filter category contains filter options of a global nature that cannot be assigned to any of the other categories.
| Filter | Explanation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Active user |
Filters orders by the person who triggers the process activated by the event. Additional settings:
|
||||||
Day of month |
Checks the day of the month on which the flow run occurs and, based on this, moves directs to the next flow step. Additional settings:
Example of how to use the filter Day of month
If the flow step is configured with these settings, the following occurs: |
||||||
Month |
Checks the month in which the flow run occurs and, based on this, directs orders to the next flow step. Additional settings:
Example of how to use the filter Month
If the flow step is configured with these settings, the following occurs: |
||||||
Weekday |
Checks the weekday on which the flow run occurs and, based on this, directs orders to the next flow step. Additional settings:
Example of how to use the filter Weekday
If the flow step is configured with these settings, the following occurs: |
Order filter category
| Filter | Explanation | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Offer valid until |
Filters orders based on their Offer valid until date. Additional settings:
Examples of using the Offer valid until filter:
If these settings apply and a flow run occurs on 10 November, then the flow step will filter only orders whose Offer valid until date is before 9 November.
If these settings apply and a flow run occurs on 10 November, then the flow step will filter only orders whose Offer valid until date is 10 November. Note: The valid until date for an offer is stored in the menu Orders » Orders » [Select order type "Offer"] » Portlet: Offer Details. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Invoice amount |
Filters orders by their invoice amount. Additional settings:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Items included |
Filters orders by contained items. Additional settings:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Open invoice amount |
Filters orders by their open invoice amount. Additional settings:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Order with return package number |
Filters orders based on whether they contain return package numbers. Additional settings:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Order tags |
Filters orders based on the tags assigned to them. Additional settings:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Order entry date (days) |
Filters orders by order entry date. Additional settings:
Examples of using the Order entry date (days) filter:
If these settings apply and a flow run occurs on 10 November, then the flow step will filter only orders whose Order entry date is before 9 November.
If these settings apply and a flow run occurs on 10 November, then the flow step will filter only orders whose Order entry date is 10 November. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Order weight |
Filters orders based on the total weight of all items contained in the order. Additional settings: Setting 1:
Setting 2:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Order status |
Filters orders by order status. Additional settings:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Order type |
Filters orders by order type. Additional settings:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Click and Collect |
Filters orders based on the shipping method Click & Collect. Additional settings:
Note: Click & Collect can only be used for orders that are referred from eBay UK and have the UK as their delivery country. For further information, refer to the chapter on Click & Collect. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
DHL Packstation/Post office |
Filters orders based on whether the delivery address contains a valid or incorrect DHL Packstation or post office. Additional settings:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Order property |
Filters orders based on their order properties. Additional settings:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Guest order |
Filters orders based on whether they are guest orders. Additional settings:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Referrer |
Filters orders by their referrer. Additional settings:
Note: The overview of the order referrers is in the menu Setup » Orders » Order referrer |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Warehouse |
Filters orders by their warehouse ID and/or warehouse type Additional settings:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Last status change (days) |
Filters data records based on the date of their last status change. Additional settings:
Examples of using the Last status change (days) filter:
If these settings apply and a flow run occurs on 10 November, then the flow step will filter only orders whose Last status change is before November 9th.
If these settings apply and a flow run occurs on 10 November, then the flow step will filter only orders whose Last status change date is November 10th. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Supplier |
Filters orders based on the assigned supplier. Additional settings:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Delivery country |
Filters orders by delivery country. Additional settings:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Dunning level |
Filters orders by dunning level. Additional settings:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Client |
Filters orders by client (Webshop). Additional settings:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Postcode |
Filters orders by postcode. Additional settings:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Redeemed coupon code |
Filters orders according to whether a specific coupon code was used for them. Additional settings:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Return date (days) |
Filters orders by return date. Additional settings:
Examples of using the Return date (days) filter:
If these settings apply and a flow run occurs on 10 November, then the flow step will filter only orders whose Return date is before November 9th.
If these settings apply and a flow run occurs on 10 November, then the flow step will filter only orders whose Return date is November 10th. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Outgoing items status |
Filters orders based on whether the goods dispatch is still open or already booked. Additional settings:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Phone number |
Filters orders by telephone number.+ Additional settings: Setting 1:
Setting 2:
Setting 3:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Loyalty program |
Filters orders by loyalty program. Additional settings:
Available loyalty programs
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Revenue |
Filters orders by revenue. Additional settings: Setting 1:
Setting 2:
Setting 3:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
VAT number |
Filters orders based on the presence of a VAT number. Additional settings:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Variations included |
Filters orders by the variations they contain. Additional settings:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Agreement of data transmission to the shipping service provider |
Filters orders based on whether an agreement for data transmission to the shipping service provider exists for them. Additional settings:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Shipping method |
Filters orders by shipping method. Additional settings:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Shipping costs |
Filters order by their gross shipping costs. Additional settings: Setting 1:
Setting 2:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Shipped |
Filters orders based on whether they are shipped, not shipped, or scheduled for future shipping. Additional settings:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Estimated delivery date (days) |
Filters orders by estimated delivery date. Additional settings:
Examples for the use of the filter Expected shipping date (Days)
If these settings apply and a flow run occurs on 10 November, then the flow step will filter only orders whose estimated delivery date is before November 9th.
If these settings apply and a flow run occurs on 10 November, then the flow step will filter only orders whose estimated delivery date is November 10th. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Estimated shipping date (days) |
Filters orders by estimated shipping date. Additional settings:
Examples for the use of the filter Expected shipping date (Days)
If these settings apply and a flow run occurs on 10 November, then the flow step will filter only orders whose estimated shipping date is before November 9th.
If these settings apply and a flow run occurs on 10 November, then the flow step will filter only orders whose estimated shipping date is November 10th. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Outgoing items booked on date (days) |
Filters data records by the date on which their outgoing items were booked. Additional settings:
Examples of using the Outgoing items booked on date (days) filter:
If these settings apply and a flow run occurs on 10 November, then the flow step will filter only orders whose*Outgoing items booked on date (days)* is before November 9th.
If these settings apply and a flow run occurs on 10 November, then the flow step will filter only orders whose*Outgoing items booked on date (days)* is November 10th. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Payment method |
Filters orders by payment method. Additional settings:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Payment due date (days) |
Filters orders by payment due date. Additional settings:
Examples of using the Offer valid until filter:
If these settings apply and a flow run occurs on 10 November, then the flow step will filter only orders whose*payment due date* is before November 9th.
If these settings apply and a flow run occurs on 10 November, then the flow step will filter only orders whose*Payment due date* is November 10th. |
Order item filter category
| Filter | Explanation |
|---|---|
Number of warehouses |
Filters orders by the number of associated warehouses. Additional settings:
|
Number of positions |
Filters orders based on the number of order items they contain. Additional settings: Setting 1:
Setting 2:
|
Order item type |
Filters orders based on the order item types they contain. Additional settings:
|
Property of the order item |
Filters orders based on the properties of the order item contained. Additional settings:
|
Quantity of order items |
Filters orders based on the number of order items of a specific order item type that they contain. Additional settings:
|
Item type included |
Filters orders based on whether they contain certain item types. Additional settings:
|
Value of order items |
Filters records by the value of the order items that they contain. Additional settings:
|
Payment filter category
| Filter | Explanation | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Payment receipt date |
Filters orders by Incoming payment date. Additional settings:
Examples of using the Payment receipt date filter:
If these settings apply and a flow run occurs on 10 November, then the flow step will filter only orders whose*incoming payment date* is November 10th.
If these settings apply and a flow run occurs on 10 November, then the flow step will filter only orders whose*incoming payment date* is 10 November. |
||||||||||||
Payment status |
Filters data sets by payment status. Additional settings:
|
6.1.1. Using AND & OR, conditions, and nested levels
| Setting | Explanation |
|---|---|
Adding conditions and sub-conditions: |
|
Condition(playlist_add) |
Use a condition to define the criteria that the orders to be filtered must meet. The first condition is already added and ready to be set. Use playlist_add to add additional conditions. |
Nested level (library_add) |
Use the nested levels to create sub-conditions within a condition. This allows you to build complex hierarchies within conditions. |
Defining the relationships between the conditions: |
|
AND |
Select AND if the orders to be filtered must meet all linked conditions. |
OR |
Select OR if the orders to be filtered must meet one of the linked conditions. |
image:
In this example, the filter first checks whether the orders meet condition 1. If this is the case, the filter then checks whether either the orders meets subcondition I or subcondition II.
6.1.2. Using operators
Use the operators listed below to define within the filter settings how the value in the order to be checked is compared with the value in the input field.
Note: For many of the filters in Flow, only some of operators listed below are available.
| Operator | Explanation |
|---|---|
= |
Is equal to |
IN |
Is in |
NIN |
Is not in. |
>= |
Is greater than or equal |
⇐ |
Is less than or equal to |
> |
Is greater than |
< |
Is less than |
[] |
Is between |
Starts with |
|
Does not start with |
|
∃ |
Exists |